Ettingshausen effect
| Thermoelectric effect |
|---|
|
Principles
Thermoelectric effect (Seebeck effect,
Peltier effect, Thomson effect) · Thermopower (Seebeck coefficient) · Ettingshausen effect · Nernst effect |
The Ettingshausen Effect (named for Albert von Ettingshausen) is a thermoelectric (or thermomagnetic) phenomenon that affects electric current in a conductor when a magnetic field is present.
The result of the phenomenon is that a potential difference is induced normal to both the direction of the magnetic field and the current.
Alternately, a temperature gradient is induced. This effect is quantified by the Ettingshausen coefficient |P|, which is defined to be
where 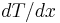 is the temperature gradient that results from the y-component
is the temperature gradient that results from the y-component 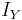 of an electric flux and the z-component
of an electric flux and the z-component 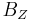 of a magnetic field.
of a magnetic field.
The reverse process is known as the Nernst effect.